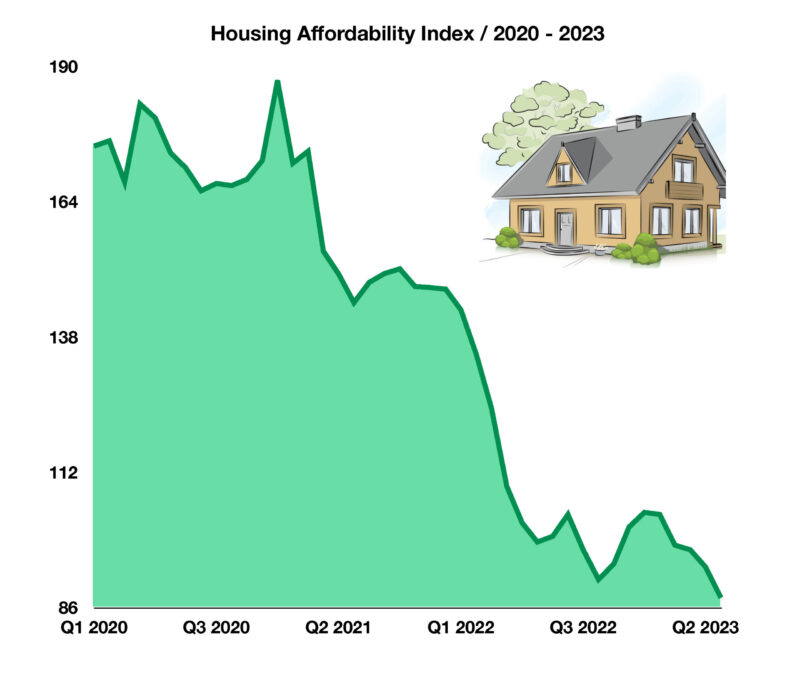
Measured by the Housing Affordability Index, the affordability of homes has been steadily eroding since early 2021. Factors affecting affordability include home prices, mortgage rates, and household incomes. With historic inflation outpacing income growth, home buyers in the U.S. have been unable to keep up with rising prices and mortgage rates.
When the Fed increases interest rates to combat inflation, mortgage rates are similarly affected. The average 30-year mortgage rate rose to a high of 7.24%, the highest since 2001. This is a significant difference to the lows reached in 2021 when the average 30-year mortgage fell to 2.65% mortgages, the lowest in U.S. history. This creates a less affordable environment for home buyers and harms potential buyers’ abilities to acquire property.
First-time buyers are forced to either buy a home knowing they may not be able to afford it or continue renting until affordability rises. For those who already own a home, remaining in their current house instead of buying a new one has been increasing in popularity as well.
Sources: National Association of Realtors, Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, Freddie Mac
Print Version: Housing Affordability Sept 2023
