Demand for products and services can vary from country to country as consumers have different choices on what they purchase. Supply constraints, transportation costs, and currency exchange rates can also affect prices among various countries and regions.
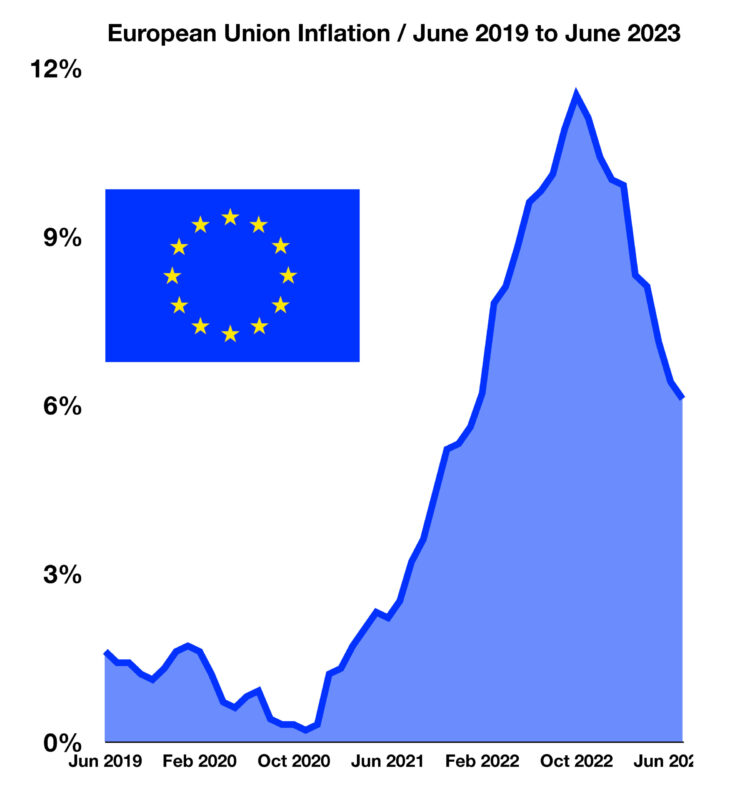
The European Union includes 27 member countries with over 448 million residents encompassing numerous cultures and languages. Similar to the United States, Europe has been experiencing an inflationary environment since 2022, propelled by supply constraints, high service costs, high energy prices, and post-pandemic demand. Inflation in the EU reached 11.5% in October 2022, surpassing the 7.7% rate in the U.S. for the same period. The most recent data available shows that the EU inflation rate had dropped to 6.1% in July 2023, down from 6.4% in June 2023.
Particular countries still have inflation rates above that of the EU, including Hungary at 19.9%, Poland at 11%, and Slovakia at 11.3%. Continued supply issues affecting energy products resulting from the war have resulted in persistent inflation for certain regions.
Sources: Eurostat, Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development
Print Version: EU Inflation Sept 2023
